Biodiversity
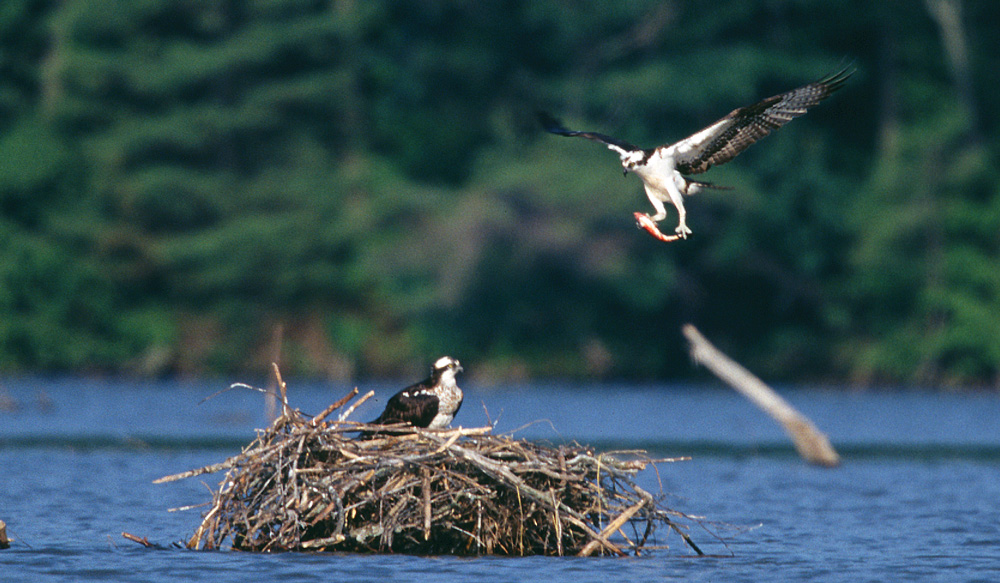

A diverse biological community is important for the function of Lake Champlain and its watershed. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of an ecosystem. Systems with a large number of species that includes plants, animals, insects and fish are typically considered “healthier” than those with fewer species. Ecosystems with a large number of species tend to be more resilient to changing climate and other pressures, including humans. Additionally, diverse ecosystems provide beneficial services to humans, including food, clean water, and recreational opportunities.
Fish and Wildlife

The Lake Champlain Basin is home to a diverse community of aquatic and terrestrial species. This diversity of creatures provides many environmental and economic benefits to the watershed. More about fish and wildlife →
Plants
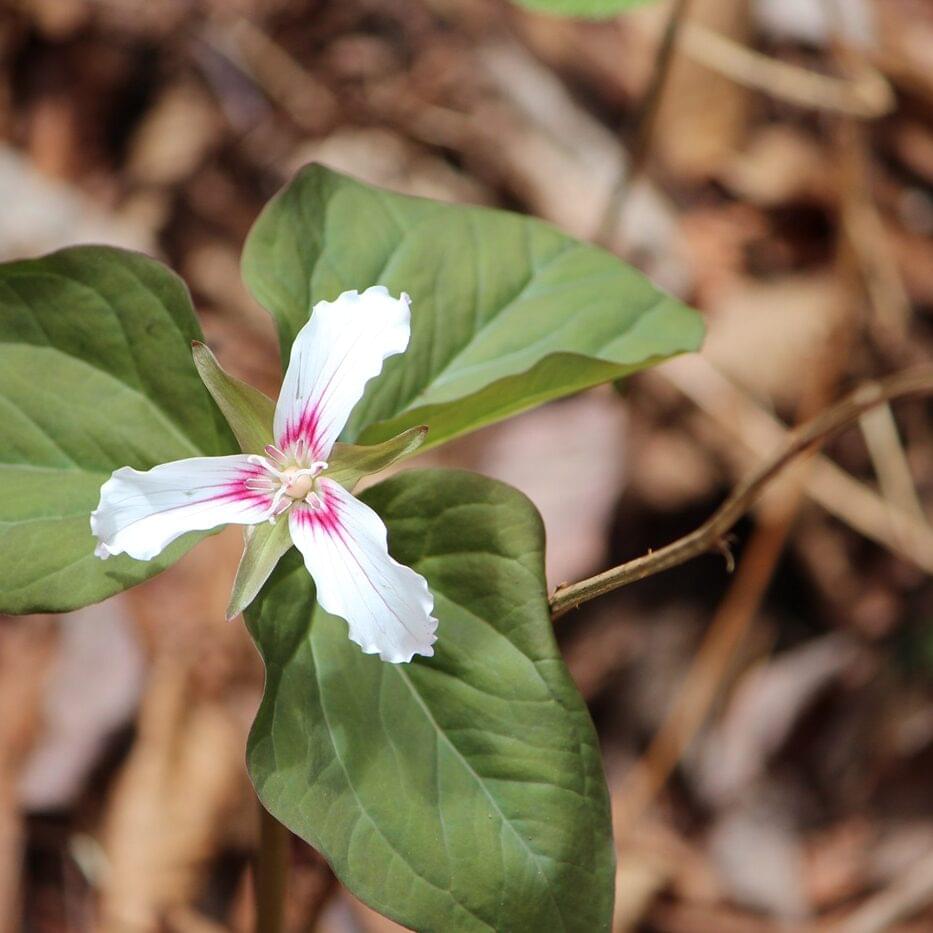

The Lake Champlain Basin supports a diverse array of natural plant communities and many rare plant species. The region is home to several plant species rarely encountered outside the region. More about plants →
Plankton
Lake Champlain’s food web links all its inhabitants, from microscopic organisms to the largest predators. At the base of this web are the most numerous organisms, primarily phytoplankton and zooplankton. More about plankton →
International Year of the Salmon
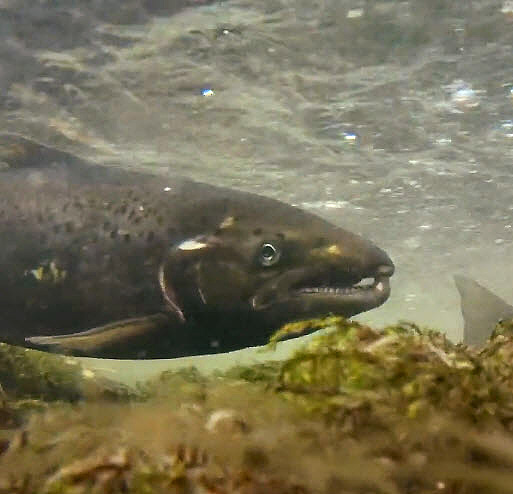

The LCBP worked with a number of partners to celebrate the International Year of the Salmon, an initiative to ensure the resilience of salmon and people throughout the Northern Hemisphere.
More about the International Year of the Salmon →
More on Biodiversity
- Vermont Wildlife Conservation
- New York State Biodiversity Clearinghouse
- Québec Biodiversity Atlas
- NatureServe
- Natural Capital Project

